- How do ZFS snapshots work?
- How do I access ZFS snapshots?
- How much space do ZFS snapshots use?
- What is ZFS snapshot?
- How do I list ZFS snapshots?
- What does ZFS stand for?
- How do I mount a zFS file system in Linux?
- How do I backup my zFS file system?
- How do I delete a dataset in zFS?
- How do I check my free space in ZFS pool?
- What is a Freenas snapshot?
- What is ZFS dataset?
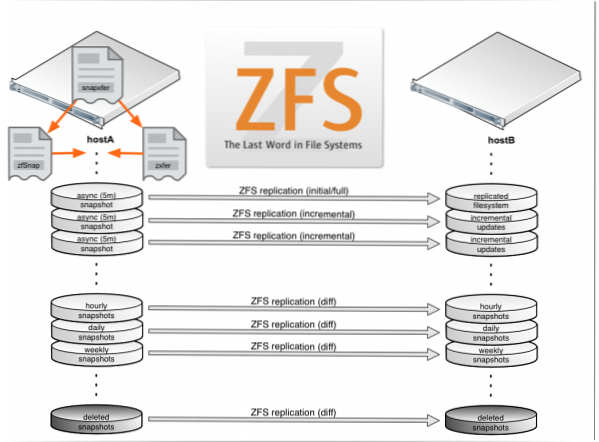
How do ZFS snapshots work?
A snapshot is a read-only copy of a file system or volume. Snapshots can be created almost instantly, and they initially consume no additional disk space within the pool. Snapshots consume disk space directly from the same storage pool as the file system or volume from which they were created. ...
How do I access ZFS snapshots?
Snapshots of file systems are accessible in the . zfs/snapshot directory within the root of the file system. For example, if tank/home/ahrens is mounted on /home/ahrens , then the tank/home/ahrens@thursday snapshot data is accessible in the /home/ahrens/. zfs/snapshot/thursday directory.
How much space do ZFS snapshots use?
The actual meta-data of snapshots are negligible. As a copy-on-write file system, ZFS snapshots only require space for modified data; creating a snapshot does not immediately duplicate everything. If you have a snapshot of given size, and then add or modify files summing up to 100GB, the snapshot will "cost" you 100GB.
What is ZFS snapshot?
zfs snapshot is a read-only copy of zfs file system or volume. They consume no extra space in the zfs pool and can be created instantly. They can be used to save a state of file system at particular point of time and can later be rolled back to exactly same state.
How do I list ZFS snapshots?
To list the snapshots created for a specific file system, enter zfs list -r -t snapshot followed by the file system name. In the example above, the snapshots created for the file system rpool/export/home are listed. This information is displayed by using the name and creation properties.
What does ZFS stand for?
ZFS stands for Zettabyte File System and is a next generation file system originally developed by Sun Microsystems for building next generation NAS solutions with better security, reliability and performance.
How do I mount a zFS file system in Linux?
File systems are mounted under /path , where path is the name of the file system. You can override the default mount point by using the zfs set command to set the mountpoint property to a specific path. ZFS automatically creates the specified mount point, if needed, and automatically mounts the associated file system.
How do I backup my zFS file system?
You can back up a zFS aggregate using a DFSMSdss logical dump.
...
Copying or performing a backup of a zFS
- Do not specify TOL(ENQF) when backing up zFS aggregates because it can cause corruption of the file system.
- Full volume dumps of volumes that contain mounted zFS file systems will not quiesce the file systems.
How do I delete a dataset in zFS?
To destroy a ZFS file system, use the zfs destroy command. By default, all of the snapshots for the dataset will be destroyed. The destroyed file system is automatically unmounted and unshared.
How do I check my free space in ZFS pool?
To see more details about used space we can run the `zfs list -o space` command. The USED and AVAIL columns we know already. The USEDSNAP is a space used by the snapshots. If we removed a file like previously this value would go up to 10.9G.
What is a Freenas snapshot?
A snapshot preserves your data exactly as it was the instant it was created. Go back to “Storage”, then “Pools”. Expand the pool to show a list of the datasets. Click the three dots on the right for the pool or dataset you want to create a snapshot for, then click “Create Snapshot”.
What is ZFS dataset?
A ZFS dataset of type filesystem that is mounted within the standard system namespace and behaves like other file systems. ... For more information about file systems, see Chapter 6, Managing Oracle Solaris ZFS File Systems. mirror. A virtual device that stores identical copies of data on two or more disks.
 Naneedigital
Naneedigital