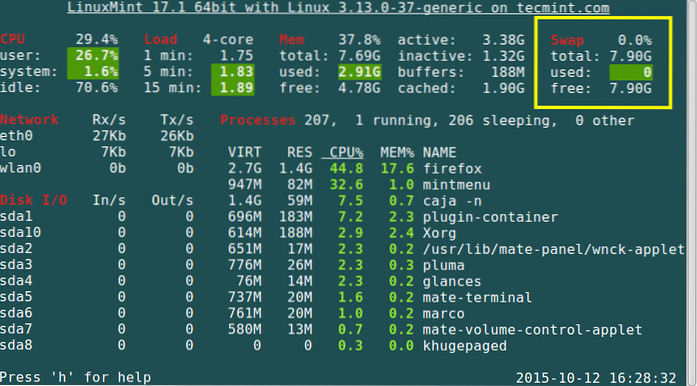
How do I check Swap space usage in Linux?
- Using the swapon Command. ...
- Using /proc/swaps which is equivalent to swapon. ...
- Using 'free' Command. ...
- Using top Command. ...
- Using atop Command. ...
- Using htop Command. ...
- Using the Glances Command. ...
- Using the vmstat Command.
- How much swap should you use in Linux?
- How do I allocate swap space in Linux?
- What is swap usage in Linux?
- How do I reduce swap usage in Linux?
- Is swap necessary for Linux?
- What is swap size in Linux?
- Can we delete swap file from Linux?
- Where is the swap file in Linux?
- Why is swap usage so high?
- What is swap usage?
- What happens when swap is full?
- Why is my swap memory full?
- How do I clear buffer in Linux?
- Should I disable swap?
How much swap should you use in Linux?
What's the right amount of swap space?
| Amount of RAM installed in system | Recommended swap space | Recommended swap space with hibernation |
|---|---|---|
| ≤ 2GB | 2X RAM | 3X RAM |
| 2GB – 8GB | = RAM | 2X RAM |
| 8GB – 64GB | 4G to 0.5X RAM | 1.5X RAM |
| >64GB | Minimum 4GB | Hibernation not recommended |
How do I allocate swap space in Linux?
The basic steps to take are simple:
- Turn off the existing swap space.
- Create a new swap partition of the desired size.
- Reread the partition table.
- Configure the partition as swap space.
- Add the new partition/etc/fstab.
- Turn on swap.
What is swap usage in Linux?
Swap is a space on a disk that is used when the amount of physical RAM memory is full. When a Linux system runs out of RAM, inactive pages are moved from the RAM to the swap space. ... In most cases, when running Linux on a virtual machine, a swap partition is not present, so the only option is to create a swap file.
How do I reduce swap usage in Linux?
To clear the swap memory on your system, you simply need to cycle off the swap. This moves all data from swap memory back into RAM. It also means that you need to be sure you have the RAM to support this operation. An easy way to do this is to run 'free -m' to see what is being used in swap and in RAM.
Is swap necessary for Linux?
Why is swap needed? ... If your system has RAM less than 1 GB, you must use swap as most applications would exhaust the RAM soon. If your system uses resource heavy applications like video editors, it would be a good idea to use some swap space as your RAM may be exhausted here.
What is swap size in Linux?
Swap space in Linux is used when the amount of physical memory (RAM) is full. If the system needs more memory resources and the RAM is full, inactive pages in memory are moved to the swap space. ... Swap space can be a dedicated swap partition (recommended), a swap file, or a combination of swap partitions and swap files.
Can we delete swap file from Linux?
Removing a Swap File From Use
- Become superuser.
- Remove the swap space. # /usr/sbin/swap -d /path/filename. ...
- Edit the /etc/vfstab file and delete the entry for the swap file.
- Recover the disk space so that you can use it for something else. # rm /path/filename. ...
- Verify that the swap file is no longer available. # swap -l.
Where is the swap file in Linux?
The procedure to check swap space usage and size in Linux is as follows:
- Open a terminal application.
- To see swap size in Linux, type the command: swapon -s .
- You can also refer to the /proc/swaps file to see swap areas in use on Linux.
- Type free -m to see both your ram and your swap space usage in Linux.
Why is swap usage so high?
Swap usage occurs when the device is running out of physical RAM and has to use virtual memory. Some swap usage is normal and nothing to worry about; you can check in Reports > System > Swap Usage to see if the amount of swap you're using is typical for your environment.
What is swap usage?
Swap usage refers to the percentage of virtual memory that is currently being used to temporarily store inactive pages from the main physical memory. It is crucial to monitor swap usage, because swap space is your “safety net” for when you run out of RAM.
What happens when swap is full?
3 Answers. Swap basically serves two roles - firstly to move out less used 'pages' out of memory into storage so memory can be used more efficiently. ... If your disks arn't fast enough to keep up, then your system might end up thrashing, and you'd experience slowdowns as data is swapped in and out of memory.
Why is my swap memory full?
Sometimes, system will use full amount of swap memory even when the system has enough physical memory available, this happens because inactive pages that are moved to swap during the high memory usage have not gone back to the physical memory in normal condition.
How do I clear buffer in Linux?
How to Clear Cache in Linux?
- Clear PageCache only. # sync; echo 1 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches.
- Clear dentries and inodes. # sync; echo 2 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches.
- Clear PageCache, dentries and inodes. # sync; echo 3 > /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches. ...
- sync will flush the file system buffer.
Should I disable swap?
By swapping out data when there is still plenty of RAM, system in its own way prepares for the situation when it might run out of RAM. So disabling swapping functionality might give you the improvement in performance because you will only be using RAM which is faster as you already said.
 Naneedigital
Naneedigital