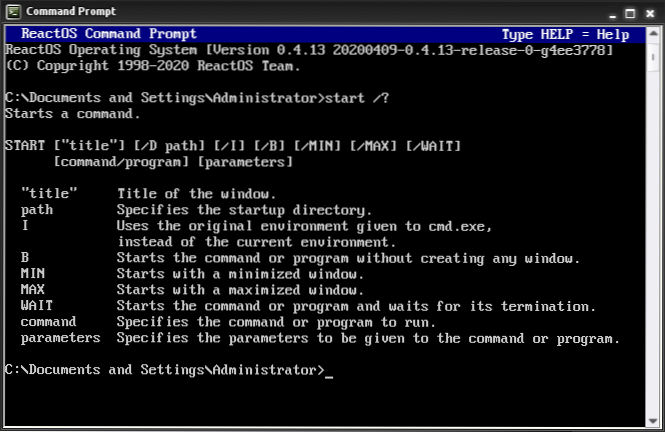
Start command can be used to run a command/batch file in another command window or to launch an application from command line. Below you can find the command's syntax and some examples. This command opens a new command prompt window.
- How do I start command prompt?
- What is start command in Windows?
- What is start command in batch?
- What is the shortcut key to open CMD?
- How do I run a text file in CMD?
- How can I shutdown another computer using CMD?
How do I start command prompt?
Press Windows+R to open “Run” box. Type “cmd” and then click “OK” to open a regular Command Prompt. Type “cmd” and then press Ctrl+Shift+Enter to open an administrator Command Prompt.
What is start command in Windows?
In computing, start is a command of the IBM OS/2, Microsoft Windows and ReactOS command-line interpreter cmd.exe (and some versions of COMMAND.COM) to start programs or batch files or to open files or directories using the default program. start is not available as a standalone program.
What is start command in batch?
In a batch script, a START command without /wait will run the program and just continue, so a script containing nothing but a START command will close the CMD console and leave the new program running. Document files can be invoked through their file association just by typing the name of the file as a command.
What is the shortcut key to open CMD?
You can also use keyboard shortcuts for this route: Windows key + X, followed by C (non-admin) or A (admin). Type cmd in the search box, then press Enter to open the highlighted Command Prompt shortcut. To open the session as an administrator, press Alt+Shift+Enter.
How do I run a text file in CMD?
On a Windows machine, we can open a text file from command prompt by just giving the file name. For example to open a text file named file1. txt, we just need to type file1. txt in the command prompt and press 'Enter'.
How can I shutdown another computer using CMD?
Type shutdown. Type \\ followed by the name of the target computer. Type /s to shutdown or /r to restart.
 Naneedigital
Naneedigital