- What are the disadvantages of biometrics?
- Do banks use biometrics?
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of biometrics?
- How reliable is biometrics?
- What is the advantage of biometrics?
- Why do we need biometrics?
- Where are biometrics used?
- What is biometric verification in bank?
- Why do banks need fingerprints?
- Can biometrics be hacked?
- Why are people reluctant to biometrics?
- What is one problem with using biometrics for identification?
What are the disadvantages of biometrics?
10 Disadvantages of Biometrics
- Physical Traits are not Changeable: Most of the biometric modalities work with physical traits such as fingerprint, iris, palm vein, etc. ...
- Error Rate: ...
- Cost: ...
- Delay: ...
- Complexity: ...
- Unhygienic: ...
- Scanning Difficulty: ...
- Physical Disability:
Do banks use biometrics?
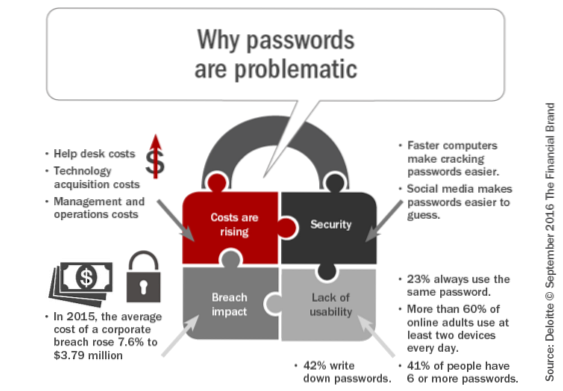
To assure the highest level of authentication security possible, many banks are leveraging biometric technology. Biometrics offer many advantages to both the financial institution and the consumer, including: ... no need for duplicate authentication processes.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of biometrics?
Despite increased security, efficiency, and convenience, biometric authentication and its uses in modern-day tech and digital applications also has disadvantages:
- Costs – Significant investment needed in biometrics for security.
- Data breaches – Biometric databases can still be hacked.
How reliable is biometrics?
According to a recent Ping Identity survey, 92 percent of enterprises rank biometric authentication as an "effective" or "very effective" to secure identity data stored on premises, and 86 percent say it is effective for protecting data stored in a public cloud.
What is the advantage of biometrics?
The advantages that biometrics provides are that the information is distinctive for every person and it can utilized as a technique for individual identification. The top benefits of Biometric technology are authentication, privacy or data discretion, authorization or access control, data veracity, and non-repudiation.
Why do we need biometrics?
Unlike the use of other forms of authentication, such as passwords or tokens, biometric recognition provides a strong link between an individual and a data record. One area where biometrics can provide substantial help is in guarding against attempts to fraudulently establish multiple identities.
Where are biometrics used?
Today, biometrics is widely used around the world for home access control, mobile phone access, vehicle access authentication and Single Sign On (SSO).
What is biometric verification in bank?
'Biometric verification' is a term being thrown around a lot these days. ... To start with, biometric verification entails you getting your fingerprints digitally scanned to make sure your data (like your CNIC) matches your bank account details.
Why do banks need fingerprints?
If you want to cash a check at a bank where you are not a customer, be prepared to bare more than a photo ID. ... To thwart fraud, Wells Fargo Bank two weeks ago began requiring all noncustomers to provide a fingerprint to cash a check drawn on the bank.
Can biometrics be hacked?
Attackers can even duplicate your biometric identification to hack into your devices or accounts. Any collection of data could easily be hacked and database consisting of a huge amount of biometrics isn't anything new. ... Stolen data could be reused to gain unauthorized access to a system.
Why are people reluctant to biometrics?
Biometric security is expensive as it involves complex procedures as well as reading the authentication and thus the unique pattern needs to be verified. this security is expensive to implement and maintain. > Users prefer passwords or pin.
What is one problem with using biometrics for identification?
The central issue is that biometric authentication technologies pose privacy and security concerns: once biometric data has been compromised, there is no way to undo the damage. For a compromised password, you simply change it; for a fingerprint, ear image, or iris scan, you're stuck with the compromised biometric.
 Naneedigital
Naneedigital