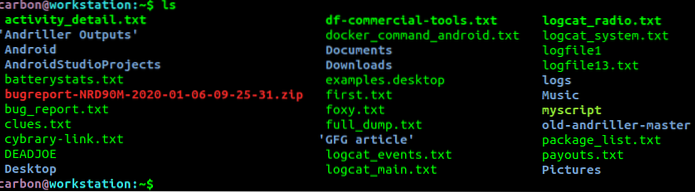
The ls command is used to list files or directories in Linux and other Unix-based operating systems. Just like you navigate in your File explorer or Finder with a GUI, the ls command allows you to list all files or directories in the current directory by default, and further interact with them via the command line.
- How do I list the contents of a directory in Linux?
- How can I get a list of files in a directory?
- Which command is used to list contents of a folder or directory?
- Which command list the contents of parent directory Linux?
- How do I open all files in a directory in Linux?
- How do you create a directory in Linux?
- How do I copy a list of file names?
- How do I print a directory?
- How do I print a list of files?
- How do I find a folder in Linux?
- Which command is used to remove a directory?
- Which command is used to display OS?
How do I list the contents of a directory in Linux?
See the following examples:
- To list all files in the current directory, type the following: ls -a This lists all files, including. dot (.) ...
- To display detailed information, type the following: ls -l chap1 .profile. ...
- To display detailed information about a directory, type the following: ls -d -l .
How can I get a list of files in a directory?
Open the command line at the folder of interest (see previous tip). Enter “dir” (without quotes) to list the files and folders contained in the folder. If you want to list the files in all the subfolders as well as the main folder, enter “dir /s” (without quotes) instead.
Which command is used to list contents of a folder or directory?
Displaying contents of a directory (ls command) Use the ls command to display the contents of a directory. The ls command writes to standard output the contents of each specified Directory or the name of each specified File, along with any other information you ask for with the flags.
Which command list the contents of parent directory Linux?
The ls is the list command in Linux. It will show the full list or content of your directory. Just type ls and press the enter key.
How do I open all files in a directory in Linux?
Open File in Linux
- Open the file using cat command.
- Open the file using less command.
- Open the file using more command.
- Open the file using nl command.
- Open the file using gnome-open command.
- Open the file using head command.
- Open the file using tail command.
How do you create a directory in Linux?
How to make a folder in Linux
- Open the terminal application in Linux.
- The mkdir command is is used to create new directories or folders.
- Say you need to create a folder name dir1 in Linux, type: mkdir dir1.
How do I copy a list of file names?
Press "Ctrl-A" and then "Ctrl-C" to copy the list of file names to your clipboard.
How do I print a directory?
1. Command DOS
- Start the Command Prompt by opening the Power Menu (Windows key + X) and selecting Command Prompt. Use the cd command to navigate to the directory you want to print. ...
- Type dir > print. txt.
- Press Enter and exit the Command Prompt.
- In File Explorer, navigate to the same folder and you should see a print.
How do I print a list of files?
To print all of the files in a folder, open that folder in Windows Explorer (File Explorer in Windows 8), press CTRL-a to select all of them, right-click any of the selected files, and select Print.
How do I find a folder in Linux?
- One can check if a directory exists in a Linux shell script using the following syntax: [ -d "/path/dir/" ] && echo "Directory /path/dir/ exists."
- You can use ! to check if a directory does not exists on Unix: [ ! -d "/dir1/" ] && echo "Directory /dir1/ DOES NOT exists."
Which command is used to remove a directory?
To remove a directory and all its contents, including any subdirectories and files, use the rm command with the recursive option, -r . Directories that are removed with the rmdir command cannot be recovered, nor can directories and their contents removed with the rm -r command.
Which command is used to display OS?
To display system information, use the uname command. Displays the operating system name as well as the system node name, operating system release, operating system version, hardware name, and processor type.
 Naneedigital
Naneedigital
![Delete Key Not Working On MacBook [Windows On Mac]](https://naneedigital.com/storage/img/images_1/delete_key_not_working_on_macbook_windows_on_mac.png)