List Of The Top System Monitoring Software
- Zabbix.
- Spiceworks Network Monitor.
- Nagios.
- OpManager by ManageEngine.
- WhatsUp Gold.
- Cacti.
- Icinga.
- OpenNMS.
- How do I monitor system activity?
- What is the difference between top and Htop?
- What is Iotop?
- Which command is used for viewing and monitoring processes graphically in Linux?
- What is system activity?
- Why is CPU so high?
- What is the use of top command in Linux?
- What is Htop in Linux?
- What is the difference between top and ps command in Linux?
- How do you run Iotop?
- How use iostat command in Linux?
- Where is Iowait on Linux?
How do I monitor system activity?
Right click the taskbar and select Task Manager or press Alt+Ctrl+Del or press Shift+Ctrl+Esc. All of them open the Windows tool. The Process tab shows the applications that are running, including ones that do not have windows and are running in the background.
What is the difference between top and Htop?
Compare top and htop
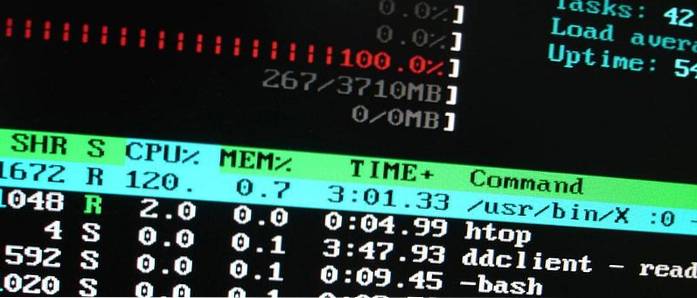
top is the default command-line utility that comes pre-installed on Linux distributions and Unix-like operating systems. It is used for displaying information about the system and its top CPU-consuming processes as well as RAM usage. ... If you take top and put it on steroids, you get htop.
What is Iotop?
Iotop is an open source and free utility similar to top command, that provides an easy way to monitor Linux Disk I/O usage details and prints a table of existing I/O utilization by process or threads on the systems.
Which command is used for viewing and monitoring processes graphically in Linux?
Show All Running Processes in Linux – ' ps' command:
We need to use the ps command. It provide information about the currently running processes, including their process identification numbers (PIDs).
What is system activity?
System Activity is an internal LookML model that connects to Looker's underlying application database. ... System Activity is designed for collecting high-volume data, and aggregating it can be used to supplement your business logs.
Why is CPU so high?
7 Answers. High CPU usage by the "System" process can often be caused by a hardware driver issue (bug, old version, incompatility etc). The System process loads (or hosts) multiple hardware drivers from different vendors that require higher level of memory access.
What is the use of top command in Linux?
top command is used to show the Linux processes. It provides a dynamic real-time view of the running system. Usually, this command shows the summary information of the system and the list of processes or threads which are currently managed by the Linux Kernel.
What is Htop in Linux?
htop is an interactive system-monitor process-viewer and process-manager. ... htop uses color and gives visual information about processor, swap and memory status. htop can also display the processes as a tree. Users often deploy htop in cases where Unix top does not provide enough information about the system's processes.
What is the difference between top and ps command in Linux?
top is mostly used interactively (try reading man page or pressing "h" while top is running) and ps is designed for non-interactive use (scripts, extracting some information with shell pipelines etc.) top allows you display of process statistics continuously until stopped vs. ps which gives you a single snapshot.
How do you run Iotop?
Important keyboard shortcuts for iotop command
- Hit the left and right arrow keys to change the sorting.
- Hit r to reverse the sorting order.
- Hit o only to see processes or threads actually doing I/O, instead of showing all processes or threads.
- Hit p only show processes.
How use iostat command in Linux?
The iostat command in Linux is used for monitoring system input/output statistics for devices and partitions. It monitors system input/output by observing the time the devices are active in relation to their average transfer rates.
Where is Iowait on Linux?
To identify whether I/O is causing system slowness you can use several commands but the easiest is the unix command top . From the CPU(s) line you can see the current percentage of CPU in I/O Wait; The higher the number the more cpu resources are waiting for I/O access.
 Naneedigital
Naneedigital