- What happens when Moore's Law ends?
- Is Moore's Law still valid in 2020?
- Why is Moore's Law no longer valid?
- How has the Moore's law changed over time?
- What will replace the transistor?
- What will replace Moore's Law?
- What is the simplest statement of the Moore's Law prediction?
- What is the limit of Moore's Law?
- Has Moore's Law slowed down?
- Why have CPU speeds stopped increasing?
- What will replace silicon chips?
- What are the three 3 things that make Moore's Law?
- What are the consequences of Moore's Law?
- What made computers smaller and faster?
What happens when Moore's Law ends?
Computer systems can still be made to be more powerful, and even with Moore's Law ending, manufacturers will still continue to build more physically powerful computer systems - just at a slower rate.
Is Moore's Law still valid in 2020?
— Moore's Law — the ability to pack twice as many transistors on the same sliver of silicon every two years — will come to an end as soon as 2020 at the 7nm node, said a keynoter at the Hot Chips conference here.
Why is Moore's Law no longer valid?
Now, some industry experts believe Moore's Law is no longer applicable. "It's over. ... In 2019, Nvidia CEO Jensen Huang declared that Moore's Law is dead and now it's more expensive and more technically difficult to double the number of transistors driving the processing power.
How has the Moore's law changed over time?
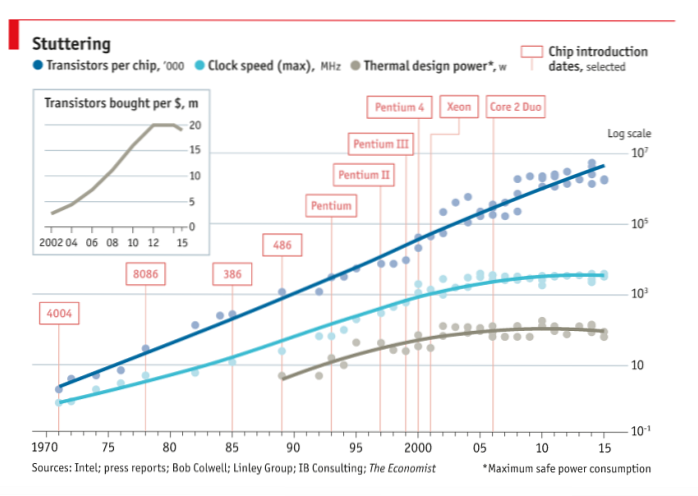
The number of transistors incorporated in a chip will approximately double every 24 months. This rate was again modified to a doubling over roughly 18 months. In its 24 month guise, Moore's Law has continued unabated for 50 years, with an overall advance of a factor of roughly 231, or 2 billion.
What will replace the transistor?
IBM aims to replace silicon transistors with carbon nanotubes to keep up with Moore's Law. A carbon nanotube that would replace a silicon transistor.
What will replace Moore's Law?
Moore's Law is being replaced by Neven's Law. Neven's law is named after Hartmut Neven, the director of Google's Quantum Artificial Intelligence Lab.
What is the simplest statement of the Moore's Law prediction?
Moore's Law refers to Moore's perception that the number of transistors on a microchip doubles every two years, though the cost of computers is halved. Moore's Law states that we can expect the speed and capability of our computers to increase every couple of years, and we will pay less for them.
What is the limit of Moore's Law?
While not a law in the mathematical sense, Moore's Law bore out: about every 18 months, a transistor would be half the size of the current transistor. This meant more transistors could be packed into a chip, which drove the exponential growth of computing power for the next 40 years.
Has Moore's Law slowed down?
2020 finds Moore's Law dramatically slowing, with processor core performance now forecasted to double every 20 years. ... Technology innovator Pliops was founded to address this gap in performance, and has developed a storage processor that enables data centers to operate faster and more efficiently.
Why have CPU speeds stopped increasing?
Why CPU Clock Speed Isn't Increasing: Heat and Power
This means more transistors can be packed into a processor. ... Transistors have become so small that Dennard scaling no longer holds. Transistors shrink, but the power required to run them increases. Thermal losses are also a major factor in chip design.
What will replace silicon chips?
Graphene is the most conductive material that material researchers know of. Microchips that use graphene can sustain many more transistors than commonly used materials like silicon. This alone will make electronics more efficient.
What are the three 3 things that make Moore's Law?
If electronics now travel half the distance to make a calculation, that means the chip is twice as fast. But the shrinking can't go on forever, and we're already starting to see three interrelated forces—size, heat, and power—threatening to slow down the Moore's Law gravy train.
What are the consequences of Moore's Law?
Economic Implications of Moore's Law. One of the economic impacts of the law is that computing devices continue to show exponential growth in complexity and computing power while effecting a comparable reduction in cost to the manufacturer and the consumer.
What made computers smaller and faster?
"These advancements were enabled by making the basic transistors in computer chips ever smaller. ... Formulated by Intel co-founder Gordon Moore, the law states that the number of transistors on a computer chip doubles about every two years, resulting in faster, smaller, and cheaper semiconductors.
 Naneedigital
Naneedigital
![Delete Key Not Working On MacBook [Windows On Mac]](https://naneedigital.com/storage/img/images_1/delete_key_not_working_on_macbook_windows_on_mac.png)
