tee Commands in Linux With Examples
- Basic Use. The basic syntax for the tee command is: [command] | tee [options] [filename] ...
- Append to the Given File. ...
- Write to Multiple Files. ...
- Hide the Output. ...
- Redirect Output of One Command to Another. ...
- Ignore Interrupts. ...
- Using tee with Sudo. ...
- Using tee in Vim Editor.
- How do I use tr in Linux?
- What does the TR command do?
- How do you append a tee?
- Does tee command overwrite?
- What is the use of awk in Linux?
- What is grep in Linux command?
- What is TR in Shell?
- What does TR mean in Linux?
- What does TR stand for?
- How do you move files in Linux?
- What do you use to forward errors to a file?
- What are special characters in Linux?
How do I use tr in Linux?
tr stands for translate.
- Syntax. The syntax of tr command is: $ tr [OPTION] SET1 [SET2]
- Translation. ...
- Convert lower case to upper case. ...
- Translate braces into parenthesis. ...
- Translate white-space to tabs. ...
- Squeeze repetition of characters using -s. ...
- Delete specified characters using -d option. ...
- Complement the sets using -c option.
What does the TR command do?
The tr command in UNIX is a command line utility for translating or deleting characters. It supports a range of transformations including uppercase to lowercase, squeezing repeating characters, deleting specific characters and basic find and replace. It can be used with UNIX pipes to support more complex translation.
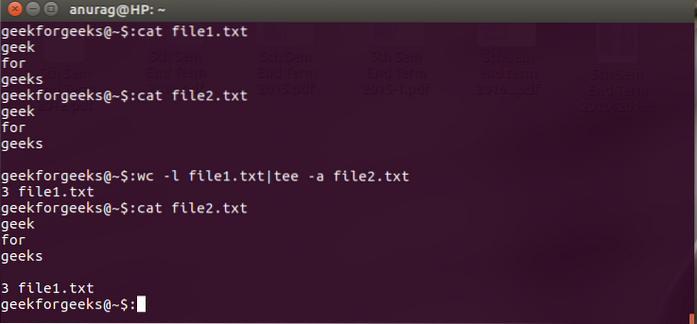
How do you append a tee?
The tee command reads from the standard input and writes to both standard output and one or more files at the same time.
...
tee Command Syntax
- -a ( --append ) - Do not overwrite the files instead append to the given files.
- -i ( --ignore-interrupts ) - Ignore interrupt signals.
- Use tee --help to view all available options.
Does tee command overwrite?
By default, the tee command will overwrite the file with the output of the initial command. Which can be overridden by using an append option using -a switch. Like with standard commands appending with >, the errors and stdout are handled differently in tee as well.
What is the use of awk in Linux?
Awk is a utility that enables a programmer to write tiny but effective programs in the form of statements that define text patterns that are to be searched for in each line of a document and the action that is to be taken when a match is found within a line. Awk is mostly used for pattern scanning and processing.
What is grep in Linux command?
What is the grep Command? Grep is an acronym that stands for Global Regular Expression Print. Grep is a Linux / Unix command-line tool used to search for a string of characters in a specified file. The text search pattern is called a regular expression. When it finds a match, it prints the line with the result.
What is TR in Shell?
tr is a command-line utility in Linux and Unix systems that translates, deletes, and squeezes characters from the standard input and writes the result to the standard output. ... Typically, it is used in combination with other commands through piping.
What does TR mean in Linux?
tr (short for translate) is a useful command line utility that translates and/or deletes characters from stdin input, and writes to stdout. It is a useful program for manipulating text on the command line. In this article, we will explain some useful tr command examples for Linux newbies.
What does TR stand for?
| Acronym | Definition |
|---|---|
| TR | Turkey |
| TR | Technical Report |
| TR | Table Row |
| TR | Trip Report |
How do you move files in Linux?
To move files, use the mv command (man mv), which is similar to the cp command, except that with mv the file is physically moved from one place to another, instead of being duplicated, as with cp. Common options available with mv include: -i -- interactive.
What do you use to forward errors to a file?
2 Answers
- Redirect stdout to one file and stderr to another file: command > out 2>error.
- Redirect stdout to a file ( >out ), and then redirect stderr to stdout ( 2>&1 ): command >out 2>&1.
What are special characters in Linux?
The characters <, >, |, and & are four examples of special characters that have particular meanings to the shell. The wildcards we saw earlier in this chapter (*, ?, and [...]) are also special characters. Table 1.6 gives the meanings of all special characters within shell command lines only.
 Naneedigital
Naneedigital