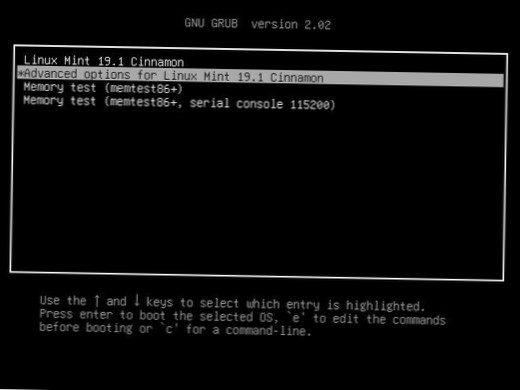
Booting Recovery Mode Quickly press either the Shift or Escape key. On newer computers it's probably Escape . The timing has to be near perfect on some computers, so you may have to press it repeatedly. With any luck you'll arrive at Ubuntu's GRUB boot menu.
- How do I boot Ubuntu into recovery mode?
- How do I boot into recovery mode?
- How do I completely reset Ubuntu?
- How do I use grub recovery?
- What is recovery mode Ubuntu?
- How do I get to the boot menu in Ubuntu?
- What is no command in recovery mode?
- How do I boot into recovery mode without the power button?
- Can not boot into TWRP recovery?
- How do I repair Ubuntu?
- How do I wipe and reinstall Ubuntu?
- What does the reset () command do?
How do I boot Ubuntu into recovery mode?
To start Ubuntu into safe mode (Recovery Mode) hold down the left Shift key as the computer starts to boot. If holding the Shift key doesn't display the menu press the Esc key repeatedly to display the GRUB 2 menu. From there you can choose the recovery option.
How do I boot into recovery mode?
How To Access Android Recovery Mode
- Turn off the phone (hold power button and select “Power Off” from the menu)
- Now, press and hold Power+Home+Volume Up buttons..
- Keep holding until device logo shows up and phone restarts again, you should enter recovery mode.
How do I completely reset Ubuntu?
There is no such thing as factory reset in ubuntu. You have to run a live disk/usb drive of any linux distro and backup your data and then reinstall ubuntu.
How do I use grub recovery?
Method 1 To Rescue Grub
- Type ls and hit enter.
- You will now see many partitions which are present on your PC. ...
- Assuming that you have installed distro in 2nd option, enter this command set prefix=(hd0,msdos1)/boot/grub (Tip: – if you don't remember the partition, try entering the command with every option.
What is recovery mode Ubuntu?
Ubuntu has come up with a clever solution in recovery mode. It lets you perform several key recovery tasks, including booting into a root terminal to give you full access to fix your computer. Note: This will only work on Ubuntu, Mint, and other Ubuntu-related distributions.
How do I get to the boot menu in Ubuntu?
If your computer uses BIOS for booting, then hold down the Shift key while GRUB is loading to get the boot menu. If your computer uses UEFI for booting, press Esc several times while GRUB is loading to get the boot menu.
What is no command in recovery mode?
You may get No command screen when Super Users Access has been denied or cancelled during the installation process of app store (Google Apps Installer widget), OS software update or when you try to reset your smartphone. In any of the cases you have to enter Android Recovery Mode and manually finish the process.
How do I boot into recovery mode without the power button?
Most of the time, one can get the recovery menu by long-pressing the Home, Power, and Volume up button simultaneously. Some other popular key combinations are Home + Volume up + Volume down, Home + Power button, Home + Power + Volume Down, and so on.
Can not boot into TWRP recovery?
Common problem installing TWRP on most Samsung devices is that on reboot, the stock recovery will overwrite TWRP. To get around it, untick Auto Reboot in Odin, flash TWRP, un plug the phone and remove the battery. Replace the battery and use the button combination to boot into recovery which should be TWRP.
How do I repair Ubuntu?
The graphical way
- Insert your Ubuntu CD, reboot your computer and set it to boot from CD in the BIOS and boot into a live session. You can also use a LiveUSB if you have created one in the past.
- Install and run Boot-Repair.
- Click "Recommended Repair".
- Now reboot your system. The usual GRUB boot menu should appear.
How do I wipe and reinstall Ubuntu?
1 Answer
- Use Ubuntu live disk to boot up.
- Select Install Ubuntu on hard disk.
- Keep on following the wizard.
- Select the Erase Ubuntu and reinstall option (the third option in the image).
What does the reset () command do?
The reset command under a BSD/Linux/UNIX operating system is used to restore a console to a normal state. This is useful after a program dies leaving a terminal in an abnormal state.
 Naneedigital
Naneedigital