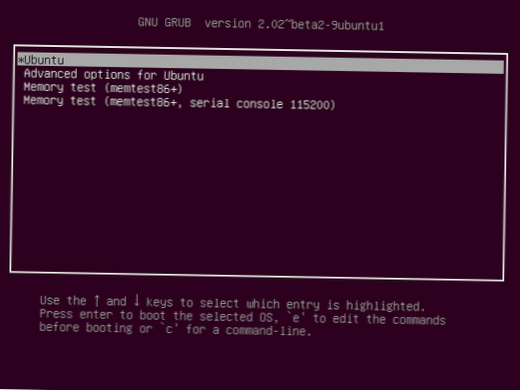
Step 2: Scan through the list to locate the Grub entry you're looking to get rid of. When you've found it, right-click on it to open up the right-click menu. Step 3: Look through the right-click menu for the “Remove” button to instantly delete the menu entry from your Grub bootloader list.
- How do I delete unwanted entries in grub?
- How do you fix a broken grub?
- How do I clean up grub menu?
- How do I edit grub menu?
- How do I remove OS boot manager?
- How do I remove old boot entries?
- How do I remove UEFI boot options?
- How do you recover grub in Linux?
- What are the grub rescue commands?
- How do I fix grub on USB?
How do I delete unwanted entries in grub?
Remove Old Kernel Entries
In the past, this meant opening up /boot/grub/menu. lst…but with Grub2, if we remove the kernel package from our computer, Grub automatically removes those options. To remove old kernel versions, open up Synaptic Package Manager, found in the System > Administration menu.
How do you fix a broken grub?
The graphical way
- Insert your Ubuntu CD, reboot your computer and set it to boot from CD in the BIOS and boot into a live session. You can also use a LiveUSB if you have created one in the past.
- Install and run Boot-Repair.
- Click "Recommended Repair".
- Now reboot your system. The usual GRUB boot menu should appear.
How do I clean up grub menu?
Clean up your grub menu from the kernels you do not use
- Determine which Kernel you are using. Just run: uname -r. and write down the result, in my case this was my output: $ uname -r 2.6.22-14-generic.
- Look for all installed kernel images. Go to /boot/ and list its contents. cd /boot ls vmlinuz* ...
- Remove the kernels you want.
How do I edit grub menu?
Once installed, search for Grub Customizer in the menu and open it.
- Start Grub Customizer.
- Select Windows Boot Manager and move it to the top.
- Once Windows is on the top, save your changes.
- Now you'll boot into Windows by default.
- Reduce the default boot time in Grub.
How do I remove OS boot manager?
Follow these steps:
- Click Start.
- Type msconfig in the search box or open Run.
- Go to Boot.
- Select which Windows version you'd like to boot into directly.
- Press Set as Default.
- You can delete the earlier version by selecting it and then clicking Delete.
- Click Apply.
- Click OK.
How do I remove old boot entries?
Open the Boot tab. You can set your default operating system, the timeout screen, and other boot options. Furthermore, you can "delete" old entries from the boot process, but this doesn't actually remove them from your system (it does stop the boot manager operating system selection screen appearing though).
How do I remove UEFI boot options?
Deleting boot options from the UEFI Boot Order list
- From the System Utilities screen, select System Configuration > BIOS/Platform Configuration (RBSU) > Boot Options > Advanced UEFI Boot Maintenance > Delete Boot Option and press Enter.
- Select one or more options from the list. Press Enter after each selection.
- Select an option and press Enter. Commit Changes and Exit.
How do you recover grub in Linux?
Method 2 To Rescue Grub
- Get a Live USB stick. I will prefer the Ubuntu Live USB stick.
- Open terminal after booting up into the live desktop.
- Mount the root partition by typing /mnt and boot to /mnt/boot and hit enter. [ e.g. sudo grub-install –root-directory=/mnt –boot-directory=/mnt/boot /dev/sda]
What are the grub rescue commands?
Normal
| Command | Result / Example |
|---|---|
| linux | Loads the kernel; insmod /vmlinuz root=(hd0,5) ro |
| loop | Mount a file as a device; loopback loop (hd0,2)/iso/my.iso |
| ls | Lists the contents of a partition/folder; ls, ls /boot/grub, ls (hd0,5)/, ls (hd0,5)/boot |
| lsmod | List loaded modules |
How do I fix grub on USB?
Resetting Grub Bootloader using a Ubuntu Live USB drive
- Try Ubuntu. ...
- Determine the Partition on Which Ubuntu is Installed Using fdisk. ...
- Determine the Partition on Which Ubuntu is Installed Using blkid. ...
- Mount The Partition with Ubuntu Installed On It. ...
- Restore Missing Grub Files Using the Grub Install Command.
 Naneedigital
Naneedigital