- How do I profile a program in Linux?
- How does Gprof work?
- How do I read GMON files?
- What is perf tool?
- How do you use valgrind for profiling?
- How do you generate GMON?
- What is Mcount?
- How do you read PERF report output?
- How do you analyze perf data?
- What does perf do in Linux?
- How do I get valgrind in Linux?
- How do I run KCacheGrind?
- How do you use valgrind?
How do I profile a program in Linux?
Using gprof to profile your applications requires the following steps:
- Compile and link the application with -pg option.
- Execute the application to generate a profile data file, default file name is gmon. out.
- Run gprof command to analyze the profile data.
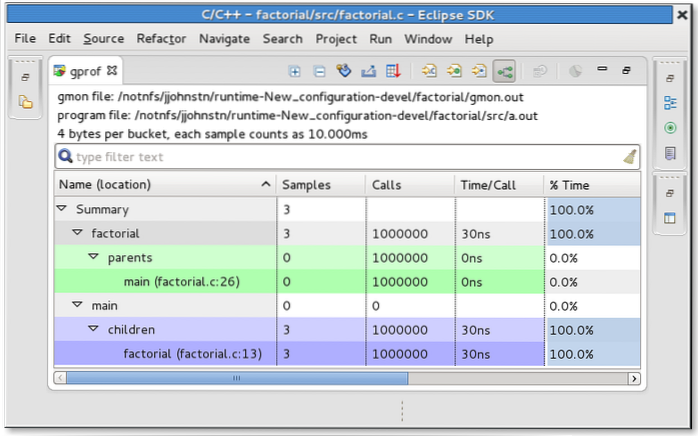
How does Gprof work?
Gprof works by automatically instrumenting your code during compilation, and then sampling the application's program counter during execution. Sampling data is saved in a file, typically named gmon. out, which can then be read by the gprof command.
How do I read GMON files?
1 Answer. gprof is the tool that reads a gmon. out file and displays information from it.
What is perf tool?
perf (sometimes called perf_events or perf tools, originally Performance Counters for Linux, PCL) is a performance analyzing tool in Linux, available from Linux kernel version 2.6. 31 in 2009.
How do you use valgrind for profiling?
To profile, you run your program under Valgrind and explicitly request the callgrind tool (if unspecified, the tool defaults to memcheck). Valgrind has written the information about the above 7 million collected events to an output file named callgrind.
How do you generate GMON?
It can be done by running the gprof command with the -c option on the call graph profile file (gmon. out by default) to generate a file (gprof.
What is Mcount?
The mcount routine, included in the profiling library, is responsible for recording in an in-memory call graph table both its parent routine (the child) and its parent's parent. This is typically done by examining the stack frame to find both the address of the child, and the return address in the original parent.
How do you read PERF report output?
perf-report(1) — Linux manual page
- NAME top. perf-report - Read perf.data (created by perf record) and display the profile.
- SYNOPSIS top. perf report [-i <file> | --input=file]
- DESCRIPTION top. This command displays the performance counter profile information recorded via perf record.
- OPTIONS top. ...
- OVERHEAD CALCULATION top. ...
- SEE ALSO top. ...
- COLOPHON top.
How do you analyze perf data?
The first step is handled by the perf record command. This command runs the program to be analyzed, collects profile data and stores the profile data into a file named perf. data (the default file name). The second step is handled by the perf report and perf annotate commands.
What does perf do in Linux?
Perf is a profiler tool for Linux 2.6+ based systems that abstracts away CPU hardware differences in Linux performance measurements and presents a simple commandline interface. Perf is based on the perf_events interface exported by recent versions of the Linux kernel.
How do I get valgrind in Linux?
You can do this by following the instructions at DebuggingProgramCrash.
- Make sure Valgrind is installed. sudo apt-get install valgrind.
- Remove any old Valgrind logs: rm valgrind.log*
- Start the program under control of memcheck:
How do I run KCacheGrind?
You can launch KCacheGrind using command line or in the program menu if your system installed it here. Then, you have to open your profile file. The first view present a list of all the profiled functions. You can see the inclusive and the self cost of each function and the location of each one.
How do you use valgrind?
To run Valgrind, pass the executable as an argument (along with any parameters to the program). The flags are, in short: --leak-check=full : "each individual leak will be shown in detail" --show-leak-kinds=all : Show all of "definite, indirect, possible, reachable" leak kinds in the "full" report.
 Naneedigital
Naneedigital