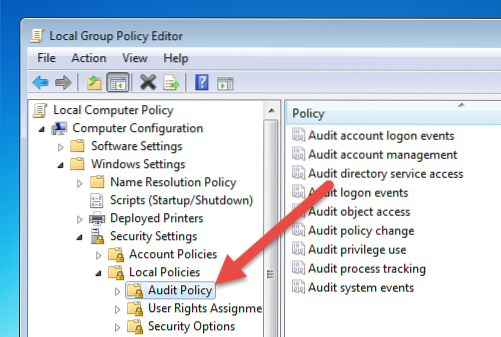
How to enable “Audit Logon Events”
- A new window of Group Policy Management Editor (GPME) will open.
- Now under Computer Configuration go to Policies node and expand it as. ...
- In the right hand panel of GPME, either Double click on “Audit logon events” or Right Click -> Properties on “Audit logon events”
- How do I audit user logon activity in Active Directory?
- How do I enable Windows auditing?
- How do I enable audit process tracking?
- How do I track user activity in Active Directory?
- How do I monitor login attempts?
- How do I view group policy logs?
- How do I know if my audit is enabled?
- How do I enable auditing in Windows 10?
- How do I know if Active Directory auditing is enabled?
- How do I monitor GPO changes?
- Why are audit policies disabled by default?
- How do I view Windows audit logs?
How do I audit user logon activity in Active Directory?
To check user login history in Active Directory, enable auditing by following the steps below:
- 1 Run gpmc. ...
- 2 Create a new GPO.
- 3 Click Edit and navigate to Computer Configuration > Policies > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Advanced Audit Policy Configuration > Audit Policies.
How do I enable Windows auditing?
- Navigate Windows Explorer to the file you want to monitor.
- Right-click on the target folder/file, and select Properties.
- Security → Advanced.
- Select the Auditing tab.
- Click Add.
- Select the Principal you want to give audit permissions to.
- In the Auditing Entry dialog box, select the types of access you want to audit.
How do I enable audit process tracking?
Right-click the appropriate Group Policy Object linked to the Domain Controllers container and select Edit. Expand the Computer Configuration → Windows Setting → Security Settings → Local Policies → Audit Policy → Audit Process Tracking.
How do I track user activity in Active Directory?
How to Track User Logon Session Time in Active Directory
- Step 1: Configure the Audit Policies. Go to “Start” ➔ “All Programs” ➔ “Administrative Tools”. Double-click “Group Policy Management” to open its window. ...
- Step 2: Track logon session using Event logs. Perform the following steps in the Event Viewer to track session time: Go to “Windows Logs” ➔ “Security”.
How do I monitor login attempts?
Expand Windows Logs and click on Security. Now, look for event ID 4624, these are successful login events for your computer. Double clicking on the event will open a popup with detailed information about that activity.
How do I view group policy logs?
The Group Policy Operational logs are displayed in the Operational object under the Applications and Services > Microsoft > Windows > GroupPolicy directory in Event Viewer. Group Policy stores some events in the Security channel of the Windows Event Log.
How do I know if my audit is enabled?
Until Oracle 10g, auditing is disabled by default, but can be enabled by setting the AUDIT_TRAIL static parameter in the init. ora file. From Oracle 11g, auditing is enabled for some system level privileges. AUDIT_TRAIL can have the following values.
How do I enable auditing in Windows 10?
The first step to auditing is to enable the auditing feature in Windows 10. To enable this, enter “CMD” in the Cortana search bar. Right-click on the Command Prompt option when it pops up and select Run as Administrator (which will require administrator credentials).
How do I know if Active Directory auditing is enabled?
Click 'Edit' in the context menu. It shows 'Group Policy Management Editor'. Go to Computer Configuration → Policies → Windows Settings → Security Settings → Advanced Audit Policy Configuration → Audit Policies. It lists all audit policies in the right pane.
How do I monitor GPO changes?
To monitor Group Policy changes, administrators must enable Group Policy change auditing and SYSVOL folder auditing. To monitor Group Policy changes completely, you must enable the auditing of DS Objects, Group Policy Container Objects and SYSVOL folder.
Why are audit policies disabled by default?
Most audit policy options are disabled by default to minimize storage requirements and system processing demands. ... When disabled, this policy allows the event to complete without an audit record being generated. When enabled, this policy stops the system when the audit file systems are full.
How do I view Windows audit logs?
To see who reads the file, open “Windows Event Viewer”, and navigate to “Windows Logs” → “Security”. There is a “Filter Current Log” option in the right pane to find the relevant events. If anyone opens the file, event ID 4656 and 4663 will be logged.
 Naneedigital
Naneedigital