- How do I check my fstab entry?
- Where is fstab located?
- How do I run fstab on Linux?
- How do I remount fstab without rebooting?
- What are the entries in fstab?
- What is the difference between fstab and MTAB?
- How do I mount fstab entry?
- Does fstab order matter?
- What is etc fstab used for?
- Which command or commands can be used to view a UUID?
- How do I mount a path in Linux?
- What are the fields in etc fstab in Linux?
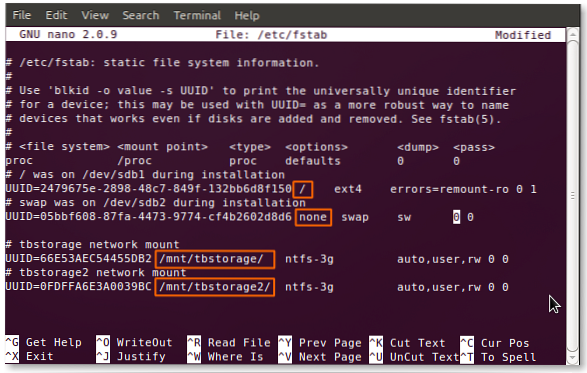
How do I check my fstab entry?
Display static filesystem information defined in fstab file. Verify /etc/fstab file contents. Verify /etc/fstab file contents and display verbose output. Verify static ext4 filesystem type information defined in particular file (mounted file systems table).
Where is fstab located?
The fstab (or file systems table) file is a system configuration file commonly found at /etc/fstab on Unix and Unix-like computer systems.
How do I run fstab on Linux?
If you're adding an entry to fstab, then you'll have to manually create the mount point before you restart your computer (and the changes take effect). Next is the section which identifies the type of file system on the partition. Many, such as ext2/3/4, ReiserFS, jFS, etc. are natively read by Linux.
How do I remount fstab without rebooting?
There is an easy way to remount all partitions from /etc/fstab without rebooting the system. This simple command remounts all file systems which specified in /etc/fstab, with the exception of partitions with the noauto option.
What are the entries in fstab?
Each entry line in the fstab file contains six fields, each one of them describes a specific information about a filesystem.
- First field - The block device. ...
- Second field - The mountpoint. ...
- Third field - The filesystem type. ...
- Fourth field - Mount options. ...
- Fifth field - Should the filesystem be dumped ? ...
- Sixth field - Fsck order.
What is the difference between fstab and MTAB?
/etc/fstab is a created by the user. It contains list of volumes to be mounted by mount . /etc/mtab is a created by the system. It contains a list of currently mounted devices.
How do I mount fstab entry?
Automatically Mounting NFS File Systems with /etc/fstab
- Set up a mount point for the remote NFS share: sudo mkdir /var/backups.
- Open the /etc/fstab file with your text editor : sudo nano /etc/fstab. Add the following line to the file: ...
- Run the mount command in one of the following forms to mount the NFS share:
Does fstab order matter?
The order of records in fstab is important because fsck(8), mount(8), and umount(8) sequentially iterate through fstab doing their thing. If you had a separate /home (or other directory) partition, it'd be mounted on-top of / , so of course / should be listed first.
What is etc fstab used for?
Your Linux system's filesystem table, aka fstab , is a configuration table designed to ease the burden of mounting and unmounting file systems to a machine. It is a set of rules used to control how different filesystems are treated each time they are introduced to a system.
Which command or commands can be used to view a UUID?
You can find the UUID of all the disk partitions on your Linux system with the blkid command. The blkid command is available by default on most modern Linux distributions. As you can see, the filesystems that has UUID are displayed.
How do I mount a path in Linux?
Mounting ISO Files
- Start by creating the mount point, it can be any location you want: sudo mkdir /media/iso.
- Mount the ISO file to the mount point by typing the following command: sudo mount /path/to/image.iso /media/iso -o loop. Don't forget to replace /path/to/image. iso with the path to your ISO file.
What are the fields in etc fstab in Linux?
/etc/fstab file
- Device – the first field specifies the mount device. ...
- Mount point – the second field specifies the mount point, the directory where the partition or disk will be mounted. ...
- File system type – the third field specifies the file system type.
- Options – the fourth field specifies the mount options.
 Naneedigital
Naneedigital