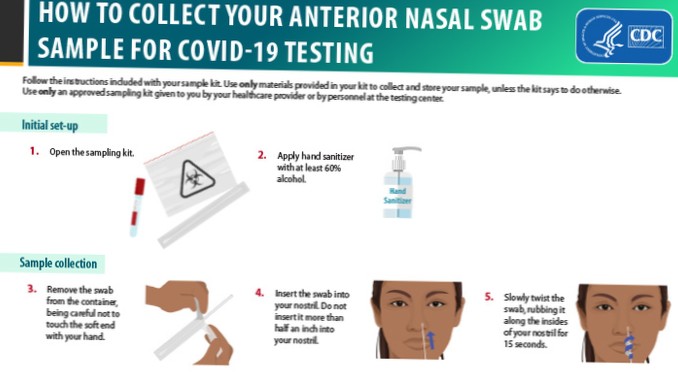
- What preventative measures can I take against the coronavirus disease?
- How can serology test be helpful in understanding the COVID-19 pandemic?
- What is the COVID-19 rapid antigen test used for?
- What is the incubation period of the coronavirus disease?
- Under what conditions does COVID-19 spread easily?
- Can the coronavirus disease spread through feces?
- Can COVID-19 cause severe disease?
- How can I help a family member with COVID-19 at home?
- What are the mild symptoms of COVID-19?
- Can the coronavirus disease be transmitted in hot or humid climates?
- How dangerous is the coronavirus disease?
- Are smokers more likely to get severe COVID-19?
What preventative measures can I take against the coronavirus disease?
To prevent infection and to slow transmission of COVID-19, do the following:
- Wash your hands regularly with soap and water, or clean them with alcohol-based hand rub.
- Maintain at least 1 metre distance between you and people coughing or sneezing.
- Avoid touching your face.
- Cover your mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing.
- Stay home if you feel unwell.
- Refrain from smoking and other activities that weaken the lungs.
- Practice physical distancing by avoiding unnecessary travel and staying away from large groups of people.
How can serology test be helpful in understanding the COVID-19 pandemic?
Serologic tests measure the antibody response in an individual. Antibodies to COVID-19 are produced over days to weeks after infection with the virus. The presence of antibodies indicates that a person was infected with the COVID-19 virus, irrespective of whether the individual had severe or mild disease, or even asymptomatic infection. Surveillance of antibody seropositivity in a population can allow inferences to be made about the extent of infection and about the cumulative incidence of infection in the population. The use of serology in epidemiology and public health research enables understanding of:
• the occurrence of infection among different populations;
• how many people have mild or asymptomatic infection, and who may not have been identified by
routine disease surveillance;
• the proportion of fatal infections among those infected;
• the proportion of the population who may be protected against infection in the future
What is the COVID-19 rapid antigen test used for?
Rapid antigen tests are commonly used in the diagnosis of respiratory illnesses. In this case, the rapid antigen detection test looks for proteins produced by the SARS-CoV-2 virus, which is the virus that causes the disease called COVID-19.
Antigen tests are immunoassays that detect the presence of a specific viral antigen, which means they identify people who currently have a viral infection. In some situations, they may be a viable alternative to nucleic acid amplification tests (NAAT or PCR tests), which look for viral RNA in the sample.
What is the incubation period of the coronavirus disease?
The incubation period of COVID-19, which is the time between exposure to the virus and symptom onset, is on average 5-6 days, but can be as long as 14 days. Thus, quarantine should be in place for 14 days from the last exposure to a confirmed case.
Under what conditions does COVID-19 spread easily?
Any situation in which people are in close proximity to one another for long periods of time increases the risk of transmission. Indoor locations, especially settings where there is poor or no ventilation, are riskier than outdoor locations.
Transmission can occur more easily in the “Three C’s”:
• Crowded places with many people nearby;
• Close-contact settings, especially where people have conversations very near each other;
• Confined and enclosed spaces with poor ventilation.
The risk of COVID-19 spreading is higher in places where these “3Cs” overlap.
Can the coronavirus disease spread through feces?
The risk of catching the COVID-19 virus from the faeces of an infected person appears to be low.
There is some evidence that the COVID-19 virus may lead to intestinal infection and be present in faeces. Approximately 2−10% of cases of confirmed COVID-19 disease presented with diarrhoea (2−4), and two studies detected COVID-19 viral RNA fragments in the faecal matter of COVID-19 patients (5,6).
However, to date only one study has cultured the COVID-19 virus from a single stool specimen (7). There have been no reports of faecal−oral transmission of the COVID-19 virus.
Can COVID-19 cause severe disease?
While COVID-19 is spreading rapidly, most people will experience only mild or moderate symptoms. That said, this coronavirus can cause severe disease in some people.
How can I help a family member with COVID-19 at home?
The ill person should stay in a separate room. If this is not possible, then keep at least a 1-metre distance from them. The sick person and anyone else in the same room should wear a medical mask.
Provide good ventilation in the room of the ill person and shared spaces, and open windows if possible and safe to do so.
What are the mild symptoms of COVID-19?
The severity of COVID-19 varies. The disease may take a mild course with few or no symptoms, resembling other common upper respiratory diseases such as the common cold.
Can the coronavirus disease be transmitted in hot or humid climates?
From the evidence so far, the COVID-19 virus can be transmitted in ALL AREAS, including areas with hot and humid weather. Regardless of climate, adopt protective measures if you live in, or travel to an area reporting COVID-19. The best way to protect yourself against COVID-19 is by frequently cleaning your hands. By doing this you eliminate viruses that may be on your hands and avoid infection that could occur by then touching your eyes, mouth, and nose.
How dangerous is the coronavirus disease?
Although for most people COVID-19 causes only mild illness, it can make some people very ill. More rarely, the disease can be fatal. Older people, and those with pre- existing medical conditions (such as high blood pressure, heart problems or diabetes) appear to be more vulnerable.
Are smokers more likely to get severe COVID-19?
Tobacco smoking is a known risk factor for many respiratory infections and increases the severity of respiratory diseases. A review of studies by public health experts convened by WHO on 29 April 2020 found that smokers are more likely to develop severe disease with COVID-19, compared to non-smokers.
COVID-19 is an infectious disease that primarily attacks the lungs. Smoking impairs lung function making it harder for the body to fight off coronaviruses and other diseases. Tobacco is also a major risk factor for noncommunicable diseases like cardiovascular disease, cancer, respiratory disease and diabetes which put people with these conditions at higher risk for developing severe illness when affected by COVID-19. Available research suggests that smokers are at higher risk of developing severe disease and death.
 Naneedigital
Naneedigital