- How does Mendeleev arrange periodic table?
- Why is Mendeleev's periodic table important?
- What are the main features of Mendeleev periodic table?
- What was wrong with Mendeleev's periodic table?
- What is the difference between Mendeleev periodic table and modern periodic table?
How does Mendeleev arrange periodic table?
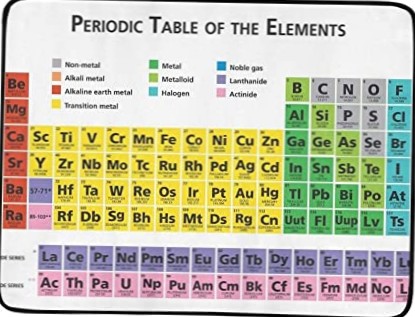
In his periodic table, Mendeleev arranged elements in rows by increasing atomic mass. Within a row, elements with lower atomic masses were on the left. Mendeleev started a new row every time the chemical properties of the elements repeated. Thus, all the elements in a column had similar properties.
Why is Mendeleev's periodic table important?
In 1869, Dmitri Mendeleev developed a method for organizing elements based on their atomic mass. ... Mendeleev's periodic table was a good model because it could be used to predict unknown elements and their properties. All of these missing elements were eventually discovered.
What are the main features of Mendeleev periodic table?
The periodic table is composed of seven horizontal rows or periods and is numbered between 1 to 7. There is a regular gradation in the properties of elements in the horizontal rows(periods) from left to right. The periodic table is composed of eight vertical columns or groups. They are numbered between 1 to 8.
What was wrong with Mendeleev's periodic table?
When Mendeleev arranged the elements in order of increasing atomic mass, the properties where repeated. ... In devising his table, Mendeleev did not conform completely to the order of atomic mass. He swapped some elements around. (We now know that the elements in the periodic table are not all in atomic mass order.)
What is the difference between Mendeleev periodic table and modern periodic table?
This law modifies the Mendeleev's periodic table into the Modern periodic table.
...
Complete step by step solution:
| Mendeleev's periodic table | Modern periodic table |
|---|---|
| Elements are arranged based on their increasing in atomic mass | Elements are arranged based on the increasing order of their atomic numbers. |
 Naneedigital
Naneedigital