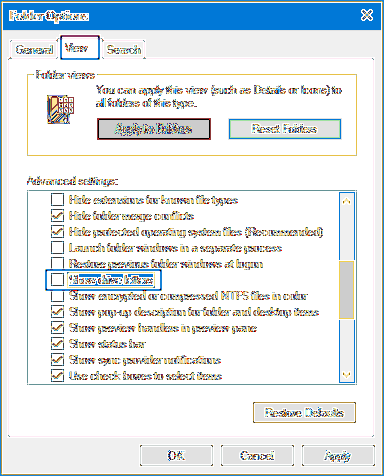
“sudo” stands for “superuser do” and it allows you to elevate your current user account to have root privilege temporarily. This is different from “su”. With “sudo”, you are still using your user account, but with root privilege, whereas in “su”, you are logged in to the root account.
- What is the difference between Sudo Su and Su?
- What does sudo su mean in Linux?
- What is Sudo And why would you use it?
- What does the su command do?
- Is it bad to use Sudo?
- What is sudo su password?
- How do I get rid of sudo su?
- Is Sudo same as root?
- What is sudo su root?
- Why is Sudo considered safer than su?
- What does Sudo mean in English?
- Why is it called Sudo?
What is the difference between Sudo Su and Su?
Sudo runs a single command with root privileges. ... This is a key difference between su and sudo. Su switches you to the root user account and requires the root account's password. Sudo runs a single command with root privileges – it doesn't switch to the root user or require a separate root user password.
What does sudo su mean in Linux?
sudo su - The sudo command allows you to run programs as another user, by default the root user. If the user is granted with sudo assess, the su command is invoked as root. Running sudo su - and then typing the user password has the same effect the same as running su - and typing the root password.
What is Sudo And why would you use it?
Whenever a user tries to install, remove or change any piece of software, he has to have the root privileges to perform such tasks. The sudo command is used to give such permissions to any particular command that a user wants to execute once the user enters a user password to give system based permissions.
What does the su command do?
The Unix command su, which stands for substitute user, is used by a computer user to execute commands with the privileges of another user account. When executed it invokes a shell without changing the current working directory or the user environment.
Is it bad to use Sudo?
When you do anything with Sudo, it means you give full rights to it, that's root access which is sometimes become very risky, if inadvertently, an app, which is running with root permission could do something wrong, results in a system crash to the corruption of the OS.
What is sudo su password?
If you want to elevate that entire command session to root privileges type 'sudo su', you will still need to enter the password to your account. Show activity on this post. Sudo password is the password that you put in the instalation of ubuntu/yours user password, if you don't have a password just click enter at all.
How do I get rid of sudo su?
Exiting From su
One is to type the word exit and then press the ENTER key. Another is to simultaneously press the CTRL and d keys.
Is Sudo same as root?
1 Answer. Executive summary: "root" is the actual name of the administrator account. "sudo" is a command which allows ordinary users to perform administrative tasks. ... Root can access any file, run any program, execute any system call, and modify any setting.
What is sudo su root?
sudo su - means run the command su as sudo which means as root. Here the system will ask you for your password since you are a sudoer. So when you offer your password then you are now working with root ability so when you run now su by the time you are using root abilities so you don't need any password.
Why is Sudo considered safer than su?
sudo allows finer grain control. One can configure sudo to give root access to some but not all commands. sudo uses the login password. This protects having to give the root password (as you would with su) and is related to the point above regarding finer grained control / access to root.
What does Sudo mean in English?
sudo (/suːduː/ or /ˈsuːdoʊ/) is a program for Unix-like computer operating systems that allows users to run programs with the security privileges of another user, by default the superuser. It originally stood for "superuser do" as the older versions of sudo were designed to run commands only as the superuser.
Why is it called Sudo?
sudo is a program for Unix-like computer operating systems that allows users to run programs with the security privileges of another user (normally the superuser, or root). Its name is a concatenation of "su" (substitute user) and "do", or take action.
 Naneedigital
Naneedigital
![Sudo vs Su [Linux] (MTE Explains)](https://naneedigital.com/storage/img/images_2/sudo_vs_su_linux_mte_explains.png)