- What is ProgramData folder used for?
- Can I delete the ProgramData folder?
- What happens if I delete ProgramData folder?
- How do I find program data folder?
- How do I view a hidden folder?
- What is package cache folder in ProgramData?
- Is it safe to delete roaming folder?
- Can I delete users folder in C drive?
- Where is the ProgramData folder in C drive?
- Can I delete ProgramData package cache?
- What can I delete in my C drive?
- Can I delete MSOCache?
What is ProgramData folder used for?
The ProgramData folder in Windows 10 contains all the data, settings, and user files that are required by the installed software and UWP apps. This directory contains application data for all users. This folder is used for application data that is not user-specific.
Can I delete the ProgramData folder?
You can delete the contents of the \ProgramData\Microsoft\Windows\Caches\ folder, and you can also delete contents of \ProgramData\Microsoft\Windows\Power Efficiency Diagnostics. ... This folder contains files used by Windows and other applications.
What happens if I delete ProgramData folder?
You shouldn't delete these, the Program Data files are files stored by the Applications you have installed on your computer. If you delete them, it will cause those programs to crash. RAM is temporary memory to keep track of the things that are open (amongst other things), it doesn't affect the storage space.
How do I find program data folder?
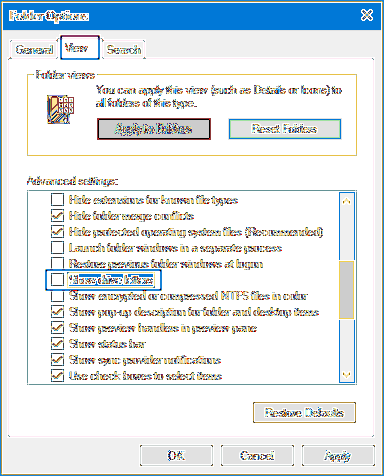
To view the "ProgramData" folder you will need to go to the Windows control panel , select "Appearance and Personalization", and find the "folder options" dialog. Select the View Tab, make the changes shown above, and click OK. You should now be able to see and access the "ProgramData" folder.
How do I view a hidden folder?
Windows® 7 and Windows® 8
- Click Start (Windows Key + Q in Windows 8).
- Click Control Panel. In category view, click Appearance and Personalization then Folder Options. In icon view, click Folder Options.
- Select the View tab.
- Select Show hidden files, folders, and drives.
- Click Apply, then click OK.
What is package cache folder in ProgramData?
Package cache is usually found in C:\ProgramData\Package Cache\ and is the source of installed packages for visual studio and other related products. ... If you delete the caches, Windows may not be able to carry out these modification operations.
Is it safe to delete roaming folder?
It is not recommended to delete Appdata\Roaming folder as it typically contains settings, temporary and cache files for many of your installed applications. In fact, once you look for the sub-folders under the name, you will find other folders related to different application installed on the computer.
Can I delete users folder in C drive?
Delete User Profile Folder via File Explorer. Open File Explorer. Go to the folder C:\Users and look for the user name which you want to delete. The appropriate folder contains everything related to the user profile, so you just need to delete this folder.
Where is the ProgramData folder in C drive?
On modern versions of Windows, you'll see a “ProgramData” folder on your system drive—usually the C:\ drive. This folder is hidden, so you'll only see it if you show hidden files in File Explorer.
Can I delete ProgramData package cache?
However, the recommendation from MICROSOFT is clearly to NOT DELETE IT. When repairing, modifying, or uninstalling a product or when installing or uninstalling a patch, if source media is required the package cache is used automatically and most users will never see a prompt.
What can I delete in my C drive?
Files that can be safely deleted from C drive:
- Temporary files.
- Download files.
- Browser's cache files.
- Old Windows log files.
- Windows upgrade files.
- Recycle Bin.
- Desktop files.
Can I delete MSOCache?
If you delete the \MSOCache folder, it will be replaced the next time any Setup operation is initiated (you will be prompted to provide the disk). So you should not delete the folder. Anytime that a patch or update is applied to Microsoft Office, the cached files will be needed.
 Naneedigital
Naneedigital