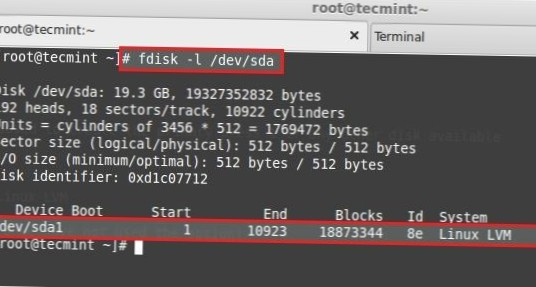
How to Extend LVM Partition with lvextend command in Linux
- Step:1 Type ' df -h' command to list the file system.
- Step:2 Now check whether free space is available space in the volume group.
- Step:3 Use lvextend command to increase the size.
- Step:3 Run the resize2fs command.
- Step:4 Use df command and verify /home size .
- How do I resize a logical volume in Linux?
- How do I shrink my LVM volume?
- How do you increase the size of logical volume?
- Can GParted resize LVM?
- How do I resize a physical volume in Linux?
- How do I resize a filesystem in Linux?
- How do I resize XFS filesystem in Linux?
- How do I reduce root partition in Linux?
- How do you remove a physical volume from a volume group?
- How do I remove logical volume?
- How do I allocate unallocated disk space in Linux?
- How do I increase the root partition size in Linux?
How do I resize a logical volume in Linux?
How to Extend Volume Group and Reduce Logical Volume
- To Create new partition Press n.
- Choose primary partition use p.
- Choose which number of partition to be selected to create the primary partition.
- Press 1 if any other disk available.
- Change the type using t.
- Type 8e to change the partition type to Linux LVM.
How do I shrink my LVM volume?
How to reduce LVM partition size in RHEL and CentOS
- Step:1 Umount the file system.
- Step:2 check the file system for Errors using e2fsck command.
- Step:3 Reduce or Shrink the size of /home to desire size.
- Step:4 Now reduce the size using lvreduce command.
- Step:5 (Optional) For the safer side, now check the reduced file system for errors.
How do you increase the size of logical volume?
To increase the size of a logical volume, use the lvextend command. When you extend the logical volume, you can indicate how much you want to extend the volume, or how large you want it to be after you extend it. The following command extends the logical volume /dev/myvg/homevol to 12 gigabytes.
Can GParted resize LVM?
Use GParted to resize the LVM physical volume. GParted won't let you shrink the LVM physical volume to a size smaller than what the unallocated space allows.
How do I resize a physical volume in Linux?
Extend LVM manually
- Extend the physical drive partition: sudo fdisk /dev/vda – Enter the fdisk tool to modify /dev/vda. ...
- Modify (extend) the LVM: Tell LVM the physical partition size has changed: sudo pvresize /dev/vda1. ...
- Resize the file system: sudo resize2fs /dev/COMPbase-vg/root.
How do I resize a filesystem in Linux?
Procedure
- If the partition the file system is on is currently mounted, unmount it. ...
- Run fsck on the unmounted file system. ...
- Shrink the file system with the resize2fs /dev/device size command. ...
- Delete and recreate the partition the file system is on to the required amount. ...
- Mount the file system and partition.
How do I resize XFS filesystem in Linux?
Create and Extend XFS filesystem based on LVM
- Step:1 Create a partition using fdisk.
- Step:2 Create LVM components : pvcreate, vgcreate and lvcreate.
- Step:3 Create XFS file system on lvm parition “/dev/vg_xfs/xfs_db”
- Step:4 Mount the xfs file system.
- Step:5 Extend the size of xfs file system.
How do I reduce root partition in Linux?
Reduce the size of root filesystem
- First, boot the system into rescue mode.
- Activate the logical volume to be reduced. ...
- Reduce the size of the file system and logical volume on /dev/VolGroup00/LogVol00. ...
- Finally reduce the size of the logical volume containing the root file system:
How do you remove a physical volume from a volume group?
To remove unused physical volumes from a volume group, use the vgreduce command. The vgreduce command shrinks a volume group's capacity by removing one or more empty physical volumes.
How do I remove logical volume?
To remove an inactive logical volume, use the lvremove command. You must close a logical volume with the umount command before it can be removed. In addition, in a clustered environment you must deactivate a logical volume before it can be removed.
How do I allocate unallocated disk space in Linux?
2 Answers
- Start a Terminal session by typing Ctrl + Alt + T.
- Type gksudo gparted and hit Enter.
- Type your password in the window that pops up.
- Find the partition Ubuntu is installed in. ...
- Right-click the partition and select Resize/Move.
- Expand the Ubuntu partition into the unallocated space.
- Profit!
How do I increase the root partition size in Linux?
7) Resizing the active root partition in Linux
Select the root partition you want to resize. In this case, we only have one partition that belongs to the root partition, so we choose to resize it. Press the Resize/Move button to resize the selected partition.
 Naneedigital
Naneedigital