- What is swap file in Linux?
- How do I swap in Linux?
- Why swap file is created in Linux?
- Where is swap file Linux?
- Is swap necessary for Linux?
- What is the swap file system?
- How do I increase memory on Linux?
- Can we delete swap file from Linux?
- How do I manage swap space in Linux?
- How do I know my swap size?
- How do I increase swap space?
- What is Mount point in Linux?
What is swap file in Linux?
Swap is a space on a disk that is used when the amount of physical RAM memory is full. When a Linux system runs out of RAM, inactive pages are moved from the RAM to the swap space. Swap space can take the form of either a dedicated swap partition or a swap file.
How do I swap in Linux?
The basic steps to take are simple:
- Turn off the existing swap space.
- Create a new swap partition of the desired size.
- Reread the partition table.
- Configure the partition as swap space.
- Add the new partition/etc/fstab.
- Turn on swap.
Why swap file is created in Linux?
A swap file allows Linux to simulate the disk space as RAM. When your system starts running out of RAM, it uses the swap space to and swaps some content of the RAM on to the disk space. This frees up the RAM to serve more important processes. ... With swap file, you don't need a separate partition anymore.
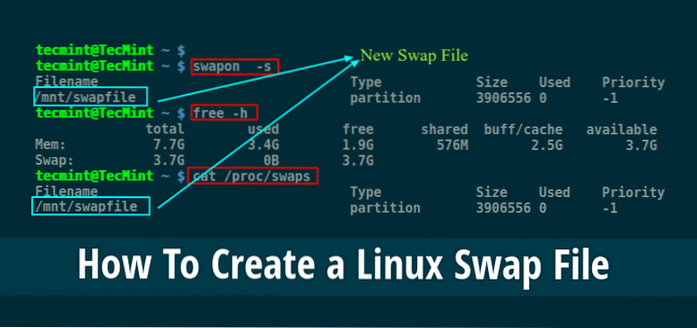
Where is swap file Linux?
The swap file is a special file in the filesystem that resides amongst your system and data files. Each line lists a separate swap space being used by the system. Here, the 'Type' field indicates that this swap space is a partition rather than a file, and from 'Filename' we see that it is on the disk sda5.
Is swap necessary for Linux?
Why is swap needed? ... If your system has RAM less than 1 GB, you must use swap as most applications would exhaust the RAM soon. If your system uses resource heavy applications like video editors, it would be a good idea to use some swap space as your RAM may be exhausted here.
What is the swap file system?
A swap file allows an operating system to use hard disk space to simulate extra memory. When the system runs low on memory, it swaps a section of RAM that an idle program is using onto the hard disk to free up memory for other programs.
How do I increase memory on Linux?
How to Increase Virtual Memory in Linux
- Determine the amount of free space available with the "df" command. ...
- Create a swap file of the size decided upon earlier with the command "sudo dd if=/dev/zero of=/mnt/swapfile bs=1M count=1024" where 1024 is the size of the swap file in megabytes and the full name of the swapfile is /mnt/swapfile.
Can we delete swap file from Linux?
Removing a Swap File From Use
- Become superuser.
- Remove the swap space. # /usr/sbin/swap -d /path/filename. ...
- Edit the /etc/vfstab file and delete the entry for the swap file.
- Recover the disk space so that you can use it for something else. # rm /path/filename. ...
- Verify that the swap file is no longer available. # swap -l.
How do I manage swap space in Linux?
Managing Swap Space in Linux
- Create a swap space. To create a swap space, an administrator need to do three things: ...
- Assign the partition type. After the swap partition, has been created, it is recommended to change the partition's type, or system ID, to 82 Linux swap. ...
- Format the device. ...
- Activate a swap space. ...
- Persistently activate swap space.
How do I know my swap size?
Check swap usage size and utilization in Linux
- Open a terminal application.
- To see swap size in Linux, type the command: swapon -s .
- You can also refer to the /proc/swaps file to see swap areas in use on Linux.
- Type free -m to see both your ram and your swap space usage in Linux.
How do I increase swap space?
How to extend LVM based swap filesystem
- Verify availability of the new space. ...
- Create additional partition for the new swap partition. ...
- Activate the new partition. ...
- Verify the new partition is available. ...
- Create a new physical volume on the LUN. ...
- Add the new volume to the volume group for the swap volume.
What is Mount point in Linux?
A mount point is a directory (typically an empty one) in the currently accessible filesystem on which an additional filesystem is mounted (i.e., logically attached). ... The mount point becomes the root directory of the newly added filesystem, and that filesystem becomes accessible from that directory.
 Naneedigital
Naneedigital