Procedure
- Create a LVM VG, if you do not have an existing one: Log into the RHEL KVM hypervisor host as root. Add a new LVM partition using the fdisk command. ...
- Create a LVM LV on the VG. For example, to create an LV called kvmVM under the /dev/VolGroup00 VG, run: ...
- Repeat the above VG and LV steps on each hypervisor host.
- How do you create a logical volume?
- How do I enable logical volume in Linux?
- How would you create a logical volume LVM and mount the file system?
- What is LVM in Linux with example?
- What is the difference between a volume and a partition?
- How do I remove logical volume?
- How do I activate the volume group?
- How do I know if my LVM is active?
- How do I know what LVM Filesystem I have?
- What is physical volume in LVM?
- Why LVM is used in Linux?
- Which command is used to create a physical volume?
How do you create a logical volume?
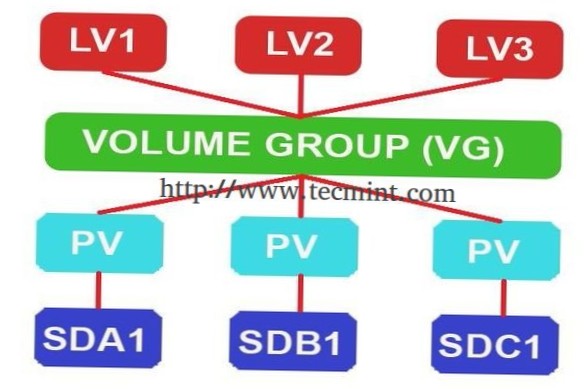
In order to create LVM logical volumes, here is a basic four step procedure:
- Create partitions to be used and initialize them as physical volumes.
- Create a volume group.
- Create a logical volume.
- Create a file system on a logical volume.
How do I enable logical volume in Linux?
The procedure to mount LVM partition in Linux as follows:
- Run vgscan command scans all supported LVM block devices in the system for VGs.
- Execute vgchange command to activate volume.
- Type lvs command to get information about logical volumes.
- Create a mount point using the mkdir command.
How would you create a logical volume LVM and mount the file system?
- Step 1: Partitioning the disk for creating Physical volume. ...
- Step 2: Creating with Physical volume (PV). ...
- Step 3: Creating with Volume Group (VG). ...
- Step 4: Creating with Logical Volume (LV). ...
- Step 5: Creating and mounting the filesystem in Linux.
What is LVM in Linux with example?
Logical Volume Management (LVM) creates a layer of abstraction over physical storage, allowing you to create logical storage volumes. ... You can think of LVM as dynamic partitions. For example, if you are running out of disk space on your server, you can just add another disk and extend the logical volume on the fly.
What is the difference between a volume and a partition?
A partition is a logical division of a hard disk. ... The main difference between a storage volume and partition is the type of disk used. A volume is created on a dynamic disk -- a logical structure that can span multiple physical disks -- while a partition is created on a basic disk.
How do I remove logical volume?
To remove an inactive logical volume, use the lvremove command. You must close a logical volume with the umount command before it can be removed. In addition, in a clustered environment you must deactivate a logical volume before it can be removed.
How do I activate the volume group?
Below is the summary of steps to perform to import new volume group with same name as that of already imported VG.
- Backup the system.
- Get the relevant volume group uuids from the system.
- Change the name of the Volume Group.
- Activate the Logical Volume Group.
- Mount the Logical Volume and verify data avilability.
How do I know if my LVM is active?
Try running lvdisplay on command line and is should display any LVM volumes if they exist. Run df on the MySQL data directory; this will return the device where the directory resides. Then run lvs or lvdisplay to check if the device is an LVM one.
How do I know what LVM Filesystem I have?
Method-1: How to Determine the File System Type on Linux Using the df Command. df command stands for Disk Filesystem that provides disk space usage information of your file systems. Use the -T option with the df command to get the file system type.
What is physical volume in LVM?
Physical volumes ( PV ) are the base "block" that you need in order to manipulate a disk using Logical Volume Manager ( LVM ). ... A physical volume is any physical storage device, such as a Hard Disk Drive ( HDD ), Solid State Drive ( SSD ), or partition, that has been initialized as a physical volume with LVM.
Why LVM is used in Linux?
LVM is a tool for logical volume management which includes allocating disks, striping, mirroring and resizing logical volumes. With LVM, a hard drive or set of hard drives is allocated to one or more physical volumes. LVM physical volumes can be placed on other block devices which might span two or more disks.
Which command is used to create a physical volume?
At least one physical volume is required to create a volume group. The command to use is vgcreate <volume group name> <device name>.
 Naneedigital
Naneedigital